Faraday effect
Faraday effect
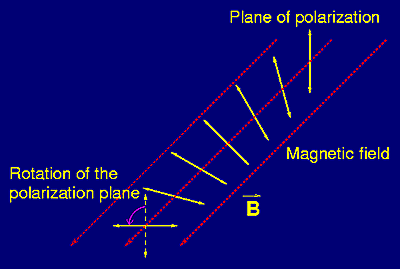
When linearly polarized light is passed through a magnetic field parallel to it, the plane of polarization is rotated. This is known as the Faraday effect or Faraday rotation. It is one example of magneto-optic phenomena.

Solids/liquids - Verdet constant
The Verdet constant is a constant that quantifies the strength of the Faraday effect for a certain material – the constant of proportionality between the angle of rotation and magnetic field.
where is the Verdet constant, is the magnetic flux density, and is the length of the path in which the fields interact.
Interstellar medium
The Faraday Effect is caused when light travels through the interstellar medium and encounters free electrons.
This time, the angle is proportional to the square of the wavelength. RM is known as the rotation measure and characterizes the effect’s strength.